12.享元模式
享元模式是一种结构型设计模式,在享元模式中,对象被设计为可共享的,可以被多个上下文使用,而不必在每个上下文中都创建新的对象。
需求
【设计模式专题之享元模式】12-图形编辑器
题目描述
- 在一个图形编辑器中,用户可以绘制不同类型的图形,包括圆形(CIRCLE)、矩形(RECTANGLE)、三角形(TRIANGLE)等。现在,请你实现一个图形绘制程序,要求能够共享相同类型的图形对象,以减少内存占用。
输入描述 输入包含多行,每行表示一个绘制命令。每个命令包括两部分:
- 图形类型(Circle、Rectangle 或 Triangle)
- 绘制的坐标位置(两个整数,分别表示 x 和 y)
输出描述
- 对于每个绘制命令,输出相应图形被绘制的位置信息。如果图形是首次绘制,输出 “drawn at”,否则输出 “shared at”。
输入示例
CIRCLE 10 20
RECTANGLE 30 40
CIRCLE 15 25
TRIANGLE 5 15
CIRCLE 10 20
RECTANGLE 30 40
输出示例
CIRCLE drawn at (10, 20)
RECTANGLE drawn at (30, 40)
CIRCLE shared at (15, 25)
TRIANGLE drawn at (5, 15)
CIRCLE shared at (10, 20)
RECTANGLE shared at (30, 40)
基础概念
享元模式是一种结构型设计模式,在享元模式中,对象被设计为可共享的,可以被多个上下文使用,而不必在每个上下文中都创建新的对象。
想要了解享元模式,就必须要区分什么是内部状态,什么是外部状态。
-
内部状态是指那些可以被多个对象共享的状态,它存储在享元对象内部,并且对于所有享元对象都是相同的,这部分状态通常是不变的。
-
而外部状态是享元对象依赖的、可能变化的部分。这部分状态不存储在享元对象内部,而是在使用享元对象时通过参数传递给对象。
举个例子,图书馆中有很多相同的书籍,但每本书都可以被多个人借阅,图书馆里的书就是内部状态,人就是外部状态。
再举个开发中的例子,假设我们在构建一个简单的图形编辑器,用户可以在画布上绘制不同类型的图形,而图形就是所有图形对象的内部状态(不变的),而图形的坐标位置就是图形对象的外部状态(变化的)。
如果图形编辑器中有成千上万的图形对象,每个图形对象都独立创建并存储其内部状态,那么系统的内存占用可能会很大,在这种情况下,享元模式共享相同类型的图形对象,每种类型的图形对象只需创建一个共享实例,然后通过设置不同的坐标位置个性化每个对象,通过共享相同的内部状态,降低了对象的创建和内存占用成本。
基本结构
享元模式包括以下几个重要角色:
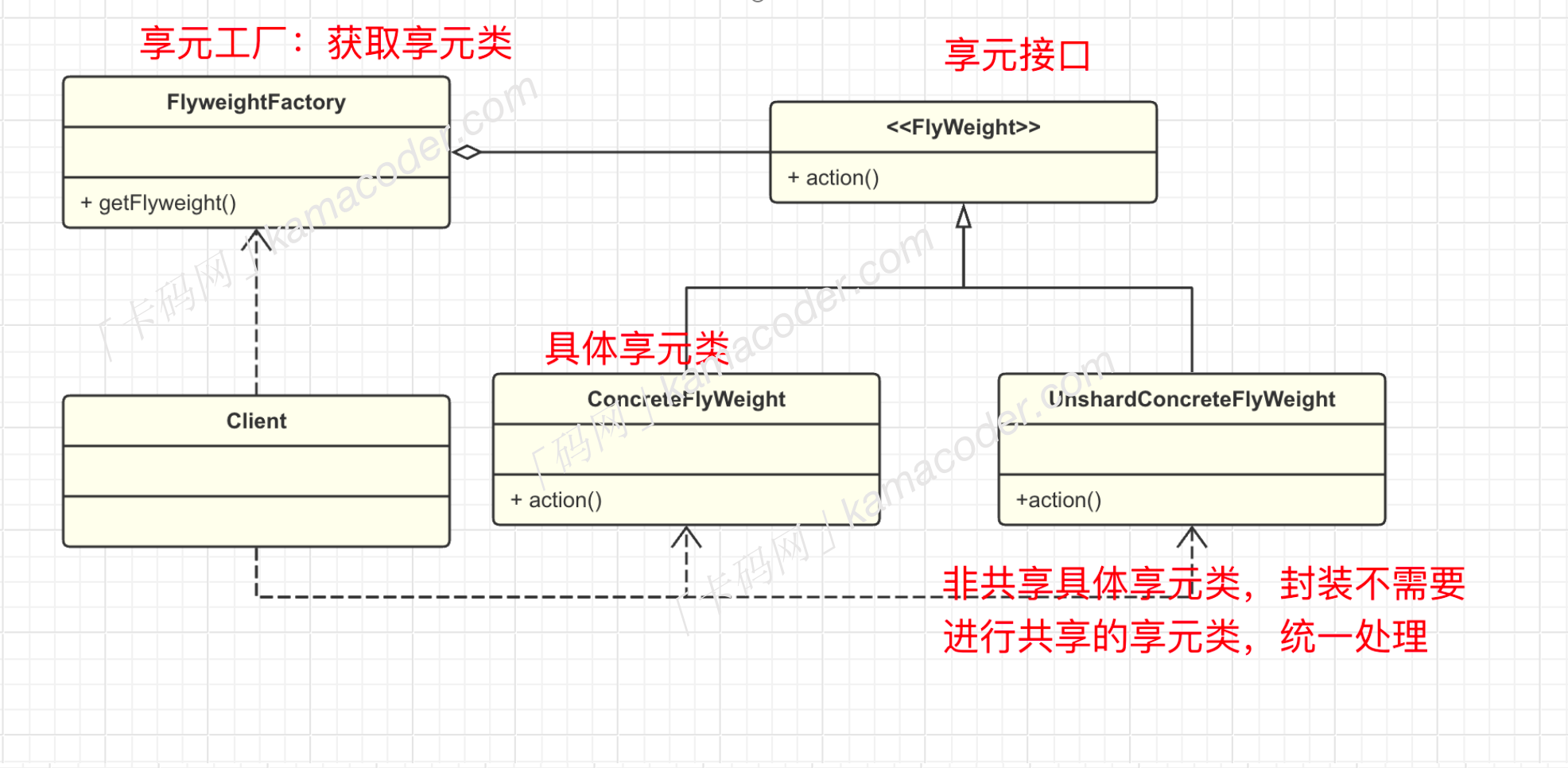
- 享元接口
Flyweight: 所有具体享元类的共享接口,通常包含对外部状态的操作。 - 具体享元类
ConcreteFlyweight: 继承Flyweight类或实现享元接口,包含内部状态。 - 享元工厂类
FlyweightFactory: 创建并管理享元对象,当用户请求时,提供已创建的实例或者创建一个。 - 客户端
Client: 维护外部状态,在使用享元对象时,将外部状态传递给享元对象。
简易实现
享元模式的实现通常涉及以下步骤:
- 定义享元接口,接受外部状态作为参数并进行处理。
// 步骤 1: 定义享元接口
interface Flyweight {
// 操作外部状态
void operation(String externalState);
}
- 实现具体享元类, 存储内部状态。
// 步骤 2: 实现具体享元类
class ConcreteFlyweight implements Flyweight {
private String intrinsicState; // 内部状态
public ConcreteFlyweight(String intrinsicState) {
this.intrinsicState = intrinsicState;
}
@Override
public void operation(String externalState) {
System.out.println("Intrinsic State: " + intrinsicState + ", External State: " + externalState);
}
}
- 创建享元工厂类,创建并管理
Flyweight对象,当用户请求一个Flyweight时,享元工厂会提供一个已经创建的实例或者创建一个。
class FlyweightFactory {
private Map<String, Flyweight> flyweights = new HashMap<>();
public Flyweight getFlyweight(String key) {
if (!flyweights.containsKey(key)) {
flyweights.put(key, new ConcreteFlyweight(key));
}
return flyweights.get(key);
}
}
- 客户端使用享元模式
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FlyweightFactory factory = new FlyweightFactory();
// 获取或创建享元对象,并传递外部状态
Flyweight flyweight1 = factory.getFlyweight("A");
flyweight1.operation("External State 1");
Flyweight flyweight2 = factory.getFlyweight("B");
flyweight2.operation("External State 2");
Flyweight flyweight3 = factory.getFlyweight("A"); // 重复使用已存在的享元对象
flyweight3.operation("External State 3");
}
}
使用场景
使用享元模式的关键在于包含大量相似对象,并且这些对象的内部状态可以共享。具体的应用场景包括文本编辑器,图形编辑器,游戏中的角色创建,这些对象的内部状态比较固定(外观,技能,形状),但是外部状态变化比较大时,可以使用。
本题代码
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
enum ShapeType {
CIRCLE, RECTANGLE, TRIANGLE
}
class Position {
private int x;
private int y;
public Position(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
}
interface Shape {
void draw(Position position);
}
class ConcreteShape implements Shape {
private ShapeType shapeType;
public ConcreteShape(ShapeType shapeType) {
this.shapeType = shapeType;
}
@Override
public void draw(Position position) {
System.out.println(shapeType + (isFirstTime ? " drawn" : " shared") + " at (" + position.getX() + ", " + position.getY() + ")");
}
private boolean isFirstTime = true;
public void setFirstTime(boolean firstTime) {
isFirstTime = firstTime;
}
}
class ShapeFactory {
private Map<ShapeType, Shape> shapes = new HashMap<>();
public Shape getShape(ShapeType type) {
if (!shapes.containsKey(type)) {
shapes.put(type, new ConcreteShape(type));
}
return shapes.get(type);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
ShapeFactory factory = new ShapeFactory();
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
String command = scanner.nextLine();
processCommand(factory, command);
}
}
private static void processCommand(ShapeFactory factory, String command) {
String[] parts = command.split(" ");
ShapeType type = ShapeType.valueOf(parts[0]);
int x = Integer.parseInt(parts[1]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(parts[2]);
Shape shape = factory.getShape(type);
shape.draw(new Position(x, y));
((ConcreteShape) shape).setFirstTime(false);
}
}
其他语言版本
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
enum ShapeType {
CIRCLE, RECTANGLE, TRIANGLE
};
std::string shapeTypeToString(ShapeType type) {
switch (type) {
case CIRCLE:
return "CIRCLE";
case RECTANGLE:
return "RECTANGLE";
case TRIANGLE:
return "TRIANGLE";
default:
return "UNKNOWN";
}
}
class Position {
private:
int x;
int y;
public:
Position(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {}
int getX() const {
return x;
}
int getY() const {
return y;
}
};
class Shape {
public:
virtual void draw(const Position &position) = 0;
virtual ~Shape() {}
};
class ConcreteShape : public Shape {
private:
ShapeType shapeType;
bool isFirstTime;
public:
ConcreteShape(ShapeType shapeType) : shapeType(shapeType), isFirstTime(true) {}
void draw(const Position &position) override {
std::cout << shapeTypeToString(shapeType) << (isFirstTime ? " drawn" : " shared") << " at (" << position.getX() << ", " << position.getY() << ")\n";
}
void setFirstTime(bool firstTime) {
isFirstTime = firstTime;
}
};
class ShapeFactory {
private:
std::unordered_map<ShapeType, Shape *> shapes;
public:
Shape *getShape(ShapeType type) {
if (shapes.find(type) == shapes.end()) {
shapes[type] = new ConcreteShape(type);
}
return shapes[type];
}
~ShapeFactory() {
for (const auto &entry : shapes) {
delete entry.second;
}
}
};
void processCommand(ShapeFactory &factory, const std::string &command);
int main() {
ShapeFactory factory;
std::string command;
while (std::getline(std::cin, command)) {
processCommand(factory, command);
}
return 0;
}
void processCommand(ShapeFactory &factory, const std::string &command) {
std::istringstream iss(command);
std::string shapeTypeStr;
int x, y;
iss >> shapeTypeStr >> x >> y;
ShapeType type;
if (shapeTypeStr == "CIRCLE") {
type = CIRCLE;
} else if (shapeTypeStr == "RECTANGLE") {
type = RECTANGLE;
} else if (shapeTypeStr == "TRIANGLE") {
type = TRIANGLE;
} else {
std::cerr << "Invalid shape type: " << shapeTypeStr << std::endl;
return;
}
Shape *shape = factory.getShape(type);
shape->draw(Position(x, y));
dynamic_cast<ConcreteShape *>(shape)->setFirstTime(false);
}
Python
from enum import Enum
from typing import Dict
class ShapeType(Enum):
CIRCLE = "CIRCLE"
RECTANGLE = "RECTANGLE"
TRIANGLE = "TRIANGLE"
class Position:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
class Shape:
def draw(self, position: Position):
pass
class ConcreteShape(Shape):
def __init__(self, shape_type: ShapeType):
self.shape_type = shape_type
self.is_first_time = True
def draw(self, position: Position):
print(f"{self.shape_type.value}{' drawn' if self.is_first_time else ' shared'} at ({position.x}, {position.y})")
def set_first_time(self, first_time: bool):
self.is_first_time = first_time
class ShapeFactory:
def __init__(self):
self.shapes: Dict[ShapeType, Shape] = {}
def get_shape(self, shape_type: ShapeType) -> Shape:
if shape_type not in self.shapes:
self.shapes[shape_type] = ConcreteShape(shape_type)
return self.shapes[shape_type]
def process_command(factory: ShapeFactory, command: str):
parts = command.split(" ")
shape_type = ShapeType(parts[0])
x = int(parts[1])
y = int(parts[2])
shape = factory.get_shape(shape_type)
shape.draw(Position(x, y))
shape.set_first_time(False)
if __name__ == "__main__":
factory = ShapeFactory()
while True:
try:
command = input()
process_command(factory, command)
except EOFError:
break
Go
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
type ShapeType int
const (
CIRCLE ShapeType = iota
RECTANGLE
TRIANGLE
)
var shapeTypeStrings = [...]string{
"CIRCLE",
"RECTANGLE",
"TRIANGLE",
}
type Position struct {
X, Y int
}
type Shape interface {
Draw(Position)
}
type ConcreteShape struct {
ShapeType ShapeType
IsFirstTime bool
}
func NewConcreteShape(shapeType ShapeType) *ConcreteShape {
return &ConcreteShape{
ShapeType: shapeType,
IsFirstTime: true,
}
}
func (s *ConcreteShape) Draw(position Position) {
fmt.Printf("%s %s at (%d, %d)\n", s.ShapeType.String(), s.getTimeDescription(), position.X, position.Y)
}
func (s *ConcreteShape) setFirstTime(firstTime bool) {
s.IsFirstTime = firstTime
}
func (s *ConcreteShape) getTimeDescription() string {
if s.IsFirstTime {
return "drawn"
}
return "shared"
}
func (st ShapeType) String() string {
if st >= 0 && int(st) < len(shapeTypeStrings) {
return shapeTypeStrings[st]
}
return "UNKNOWN"
}
type ShapeFactory struct {
shapes map[ShapeType]Shape
}
func NewShapeFactory() *ShapeFactory {
return &ShapeFactory{
shapes: make(map[ShapeType]Shape),
}
}
func (f *ShapeFactory) getShape(shapeType ShapeType) Shape {
if _, exists := f.shapes[shapeType]; !exists {
f.shapes[shapeType] = NewConcreteShape(shapeType)
}
return f.shapes[shapeType]
}
func main() {
var factory = NewShapeFactory()
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(os.Stdin)
for scanner.Scan() {
command := scanner.Text()
processCommand(factory, command)
}
if err := scanner.Err(); err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error reading standard input:", err)
}
}
func processCommand(factory *ShapeFactory, command string) {
parts := splitCommand(command)
shapeType := ShapeTypeFromString(parts[0])
x, _ := strconv.Atoi(parts[1])
y, _ := strconv.Atoi(parts[2])
shape := factory.getShape(shapeType)
shape.Draw(Position{X: x, Y: y})
concreteShape, ok := shape.(*ConcreteShape)
if ok {
concreteShape.setFirstTime(false)
}
}
func splitCommand(command string) []string {
return splitWithoutEmpty(command, ' ')
}
func splitWithoutEmpty(s string, sep byte) []string {
parts := strings.FieldsFunc(s, func(r rune) bool {
return r == rune(sep)
})
return parts
}
func ShapeTypeFromString(s string) ShapeType {
for i, str := range shapeTypeStrings {
if str == s {
return ShapeType(i)
}
}
return CIRCLE
}