8.装饰模式
通常情况下,扩展类的功能可以通过继承实现,但是扩展越多,子类越多,装饰模式可以在不定义子类的情况下动态的给对象添加一些额外的功能。
需求
【设计模式专题装饰模式】8-咖啡加糖
题目描述
- 小明喜欢品尝不同口味的咖啡,他发现每种咖啡都可以加入不同的调料,比如牛奶、糖和巧克力。他决定使用装饰者模式制作自己喜欢的咖啡。
- 请设计一个简单的咖啡制作系统,使用装饰者模式为咖啡添加不同的调料。系统支持两种咖啡类型:黑咖啡(Black Coffee)和拿铁(Latte)。
输入描述
- 多行输入,每行包含两个数字。第一个数字表示咖啡的选择(1 表示黑咖啡,2 表示拿铁),第二个数字表示要添加的调料类型(1 表示牛奶,2 表示糖)。
输出描述
- 根据每行输入,输出制作咖啡的过程,包括咖啡类型和添加的调料。
输入示例
1 1
2 2
输出示例
Brewing Black Coffee
Adding Milk
Brewing Latte
Adding Sugar
基本概念
通常情况下,扩展类的功能可以通过继承实现,但是扩展越多,子类越多,装饰模式(Decorator Pattern, 结构型设计模式)可以在**不定义子类的情况下动态的给对象添加一些额外的功能。**具体的做法是将原始对象放入包含行为的特殊封装类(装饰类),从而为原始对象动态添加新的行为,而无需修改其代码。
举个简单的例子,假设你有一个基础的图形类,你想要为图形类添加颜色、边框、阴影等功能,如果每个功能都实现一个子类,就会导致产生大量的类,这时就可以考虑使用装饰模式来动态地添加,而不需要修改图形类本身的代码,这样可以使得代码更加灵活、更容易维护和扩展。
基本结构:
装饰模式包含以下四个主要角色:
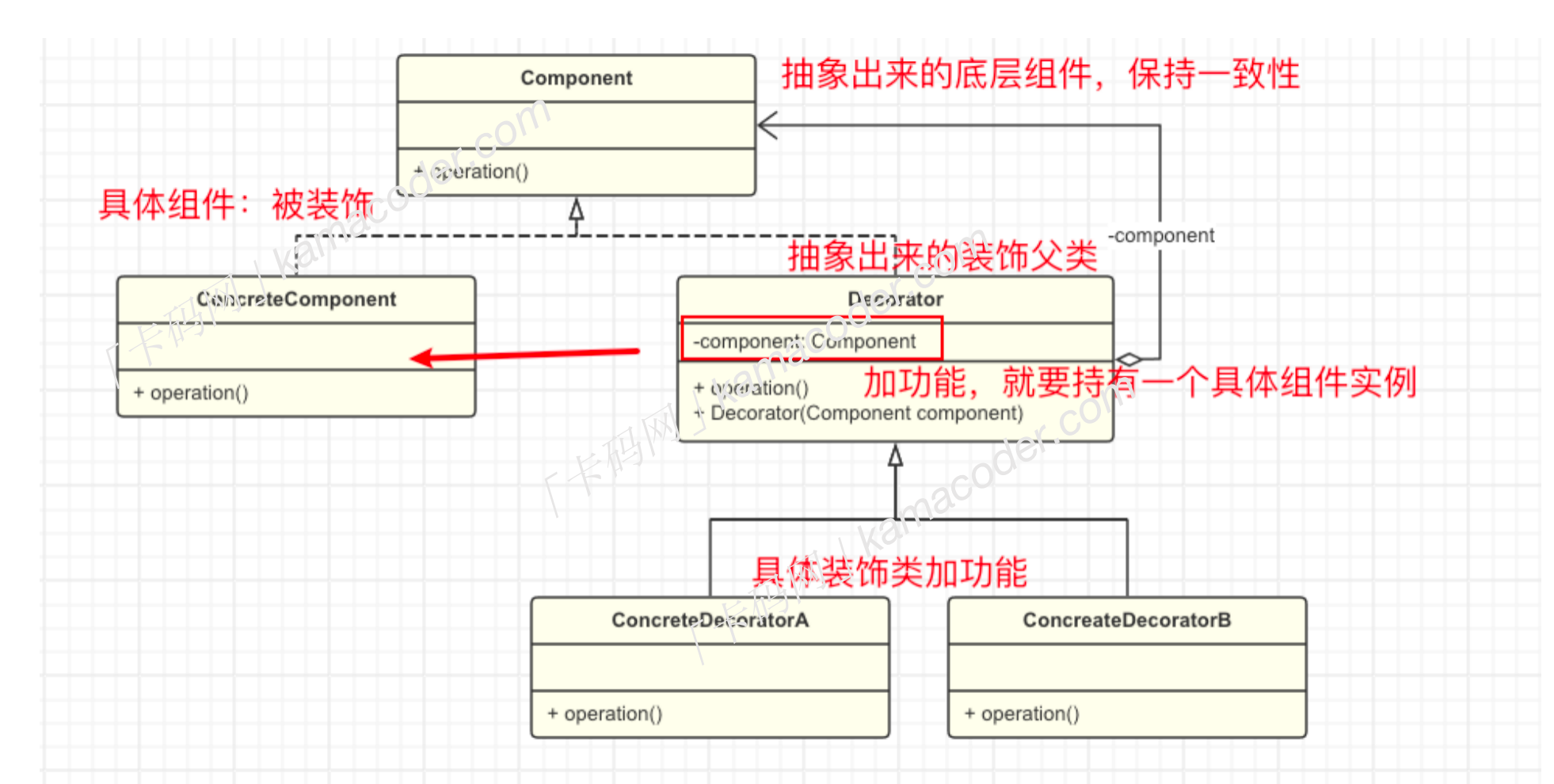
- 组件
Component:通常是抽象类或者接口,是具体组件和装饰者的父类,定义了具体组件需要实现的方法,比如说我们定义Coffee为组件。 - 具体组件
ConcreteComponent: 实现了Component接口的具体类,是被装饰的对象。 - 装饰类
Decorator: 一个抽象类,给具体组件添加功能,但是具体的功能由其子类具体装饰者完成,持有一个指向Component对象的引用。 - 具体装饰类
ConcreteDecorator: 扩展Decorator类,负责向Component对象添加新的行为,加牛奶的咖啡是一个具体装饰类,加糖的咖啡也是一个具体装饰类。
基本实现
装饰模式的实现包括以下步骤:
- 定义Component接口
// 组件接口
public interface Component {
void operation();
}
- 实现 ConcreteComponent
// 具体组件
public class ConcreteComponent implements Component {
@Override
public void operation() {
System.out.println("ConcreteComponent operation");
}
}
- 定义Decorator装饰类,继承自Component
// 定义一个抽象的装饰者类,继承自Component
public abstract class Decorator implements Component {
protected Component component;
public Decorator(Component component) {
this.component = component;
}
@Override
public void operation() {
component.operation();
}
}
- 定义具体的装饰者实现,给具体组件对象添加功能。
// 具体的装饰者实现
public class ConcreteDecorator extends Decorator {
public ConcreteDecorator(Component component) {
super(component);
}
// 根据需要添加额外的方法
@Override
public void operation() {
// 可以在调用前后添加额外的行为
System.out.println("Before operation in ConcreteDecorator");
super.operation();
System.out.println("After operation in ConcreteDecorator");
}
}
- 在客户端使用
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建具体组件
Component concreteComponent = new ConcreteComponent();
// 使用具体装饰者包装具体组件
Decorator decorator = new ConcreteDecorator(concreteComponent);
// 调用操作
decorator.operation();
}
}
应用场景
装饰模式通常在以下几种情况使用:
-
当需要给一个现有类添加附加功能,但由于某些原因不能使用继承来生成子类进行扩充时,可以使用装饰模式。
-
动态的添加和覆盖功能:当对象的功能要求可以动态地添加,也可以再动态地撤销时可以使用装饰模式。
在Java的I/O库中,装饰者模式被广泛用于增强I/O流的功能。例如,BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream这两个类提供了缓冲区的支持,通过在底层的输入流和输出流上添加缓冲区,提高了读写的效率,它们都是InputStream和OutputStream的装饰器。BufferedReader和BufferedWriter这两个类与BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream类似,提供了字符流的缓冲功能,是Reader和Writer的装饰者。
本题代码
import java.util.Scanner;
// 咖啡接口
interface Coffee {
void brew();
}
// 具体的黑咖啡类
class BlackCoffee implements Coffee {
@Override
public void brew() {
System.out.println("Brewing Black Coffee");
}
}
// 具体的拿铁类
class Latte implements Coffee {
@Override
public void brew() {
System.out.println("Brewing Latte");
}
}
// 装饰者抽象类
abstract class Decorator implements Coffee {
protected Coffee coffee;
public Decorator(Coffee coffee) {
this.coffee = coffee;
}
@Override
public void brew() {
coffee.brew();
}
}
// 具体的牛奶装饰者类
class MilkDecorator extends Decorator {
public MilkDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
@Override
public void brew() {
super.brew();
System.out.println("Adding Milk");
}
}
// 具体的糖装饰者类
class SugarDecorator extends Decorator {
public SugarDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
@Override
public void brew() {
super.brew();
System.out.println("Adding Sugar");
}
}
// 客户端代码
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
int coffeeType = scanner.nextInt();
int condimentType = scanner.nextInt();
// 根据输入制作咖啡
Coffee coffee;
if (coffeeType == 1) {
coffee = new BlackCoffee();
} else if (coffeeType == 2) {
coffee = new Latte();
} else {
System.out.println("Invalid coffee type");
continue;
}
// 根据输入添加调料
if (condimentType == 1) {
coffee = new MilkDecorator(coffee);
} else if (condimentType == 2) {
coffee = new SugarDecorator(coffee);
} else {
System.out.println("Invalid condiment type");
continue;
}
// 输出制作过程
coffee.brew();
}
}
}
其他语言版本
Java
将处理输入和创建对象的逻辑分离到方法中。
import java.util.Scanner;
// 定义咖啡接口
interface Coffee {
void execute();
}
// 黑咖啡类,实现咖啡接口
class BrewingBlackCoffee implements Coffee {
@Override
public void execute() {
System.out.println("Brewing Black Coffee");
}
}
// 拿铁类,实现咖啡接口
class BrewingLatte implements Coffee {
@Override
public void execute() {
System.out.println("Brewing Latte");
}
}
// 咖啡装饰器抽象类,实现咖啡接口
abstract class Decorator implements Coffee {
private Coffee coffee;
public Decorator(Coffee coffee) {
this.coffee = coffee;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
coffee.execute();
}
}
// 牛奶装饰器类,继承自装饰器类
class MilkDecorator extends Decorator {
public MilkDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
@Override
public void execute() {
super.execute();
System.out.println("Adding Milk");
}
}
// 糖装饰器类,继承自装饰器类
class SugarDecorator extends Decorator {
public SugarDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
@Override
public void execute() {
super.execute();
System.out.println("Adding Sugar");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
String input;
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
input = scanner.nextLine();
if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) {
break;
}
processInput(input);
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("输入格式无效:" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
scanner.close();
}
}
// 处理输入的方法
private static void processInput(String input) {
String[] parts = input.split(" ");
if (parts.length != 2) {
System.out.println("输入格式无效。请提供两个数字,中间用空格分隔。");
return;
}
try {
int type1 = Integer.parseInt(parts[0]);
int type2 = Integer.parseInt(parts[1]);
Coffee coffee = createCoffee(type1);
if (coffee == null) {
System.out.println("咖啡类型无效。请输入1(黑咖啡)或2(拿铁)。");
return;
}
coffee = decorateCoffee(coffee, type2);
if (coffee == null) {
System.out.println("装饰类型无效。请输入1(牛奶)或2(糖)。");
return;
}
coffee.execute();
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("输入格式无效:两个输入都必须是数字。");
}
}
// 创建咖啡对象的方法
private static Coffee createCoffee(int type) {
switch (type) {
case 1:
return new BrewingBlackCoffee();
case 2:
return new BrewingLatte();
default:
return null;
}
}
// 添加装饰器的方法
private static Coffee decorateCoffee(Coffee coffee, int type) {
switch (type) {
case 1:
return new MilkDecorator(coffee);
case 2:
return new SugarDecorator(coffee);
default:
return null;
}
}
}
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
// 咖啡接口
class Coffee {
public:
virtual ~Coffee() {}
virtual void brew() = 0;
};
// 具体的黑咖啡类
class BlackCoffee : public Coffee {
public:
void brew() override {
std::cout << "Brewing Black Coffee" << std::endl;
}
};
// 具体的拿铁类
class Latte : public Coffee {
public:
void brew() override {
std::cout << "Brewing Latte" << std::endl;
}
};
// 装饰者抽象类
class Decorator : public Coffee {
protected:
std::unique_ptr<Coffee> coffee;
public:
Decorator(std::unique_ptr<Coffee> coffee) : coffee(std::move(coffee)) {}
void brew() override {
if (coffee) {
coffee->brew();
}
}
};
// 具体的牛奶装饰者类
class MilkDecorator : public Decorator {
public:
MilkDecorator(std::unique_ptr<Coffee> coffee) : Decorator(std::move(coffee)) {}
void brew() override {
Decorator::brew();
std::cout << "Adding Milk" << std::endl;
}
};
// 具体的糖装饰者类
class SugarDecorator : public Decorator {
public:
SugarDecorator(std::unique_ptr<Coffee> coffee) : Decorator(std::move(coffee)) {}
void brew() override {
Decorator::brew();
std::cout << "Adding Sugar" << std::endl;
}
};
// 客户端代码
int main() {
int coffeeType, condimentType;
while (std::cin >> coffeeType >> condimentType) {
// 根据输入制作咖啡
std::unique_ptr<Coffee> coffee;
if (coffeeType == 1) {
coffee = std::make_unique<BlackCoffee>();
} else if (coffeeType == 2) {
coffee = std::make_unique<Latte>();
} else {
std::cout << "Invalid coffee type" << std::endl;
continue;
}
// 根据输入添加调料
if (condimentType == 1) {
coffee = std::make_unique<MilkDecorator>(std::move(coffee));
} else if (condimentType == 2) {
coffee = std::make_unique<SugarDecorator>(std::move(coffee));
} else {
std::cout << "Invalid condiment type" << std::endl;
continue;
}
// 输出制作过程
coffee->brew();
}
return 0;
}
Python
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from typing import Type
# 咖啡接口
class Coffee(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def brew(self):
pass
# 具体的黑咖啡类
class BlackCoffee(Coffee):
def brew(self):
print("Brewing Black Coffee")
# 具体的拿铁类
class Latte(Coffee):
def brew(self):
print("Brewing Latte")
# 装饰者抽象类
class Decorator(Coffee, ABC):
def __init__(self, coffee: Type[Coffee]):
self._coffee = coffee
def brew(self):
self._coffee.brew()
# 具体的牛奶装饰者类
class MilkDecorator(Decorator):
def brew(self):
super().brew()
print("Adding Milk")
# 具体的糖装饰者类
class SugarDecorator(Decorator):
def brew(self):
super().brew()
print("Adding Sugar")
# 客户端代码
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
while True:
coffee_type, condiment_type = map(int, input().split())
# 根据输入制作咖啡
if coffee_type == 1:
coffee = BlackCoffee()
elif coffee_type == 2:
coffee = Latte()
else:
print("Invalid coffee type")
continue
# 根据输入添加调料
if condiment_type == 1:
coffee = MilkDecorator(coffee)
elif condiment_type == 2:
coffee = SugarDecorator(coffee)
else:
print("Invalid condiment type")
continue
# 输出制作过程
coffee.brew()
except EOFError:
pass
Go
package main
import "fmt"
// 咖啡接口
type Coffee interface {
brew()
}
// 具体的黑咖啡类
type BlackCoffee struct{}
func (bc *BlackCoffee) brew() {
fmt.Println("Brewing Black Coffee")
}
// 具体的拿铁类
type Latte struct{}
func (l *Latte) brew() {
fmt.Println("Brewing Latte")
}
// 装饰者抽象类
type Decorator struct {
coffee Coffee
}
func (d *Decorator) brew() {
d.coffee.brew()
}
// 具体的牛奶装饰者类
type MilkDecorator struct {
Decorator
}
func (md *MilkDecorator) brew() {
md.Decorator.brew()
fmt.Println("Adding Milk")
}
// 具体的糖装饰者类
type SugarDecorator struct {
Decorator
}
func (sd *SugarDecorator) brew() {
sd.Decorator.brew()
fmt.Println("Adding Sugar")
}
func main() {
for {
var coffeeType, condimentType int
if _, err := fmt.Scan(&coffeeType, &condimentType); err != nil {
break
}
// 根据输入制作咖啡
var coffee Coffee
if coffeeType == 1 {
coffee = &BlackCoffee{}
} else if coffeeType == 2 {
coffee = &Latte{}
} else {
fmt.Println("Invalid coffee type")
continue
}
// 根据输入添加调料
if condimentType == 1 {
coffee = &MilkDecorator{Decorator: Decorator{coffee: coffee}}
} else if condimentType == 2 {
coffee = &SugarDecorator{Decorator: Decorator{coffee: coffee}}
} else {
fmt.Println("Invalid condiment type")
continue
}
// 输出制作过程
coffee.brew()
}
}