On this page
article
4.Vue
一套用于快速构建用户界面的渐进式前端框架
1.Vue介绍

- Vue.js:简称Vue,是一套用于快速构建用户界面的渐进式前端框架。
- Vue.js核心实现
- 响应式数据绑定:当数据发生改变,视图可以自动更新,不用关心DOM操作,专心数据操作。
- 可组合的视图组件:把视图按照功能切分成若干个基本单元,可维护,可重用,可测试等特点。
- 响应式,双向数据绑定,即MVVM。是指数据层(Model)-视图层(View)-数据视图(ViewModel)的响应式框架。
1.2引入Vue.js
- 在html中使用CDN包的形式引入
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"><script>
- 下载js文件保存到本地再导入
- 使用npm安装
npm install @vue/cli@4.5.12
- 使用官方vuecli脚手架创建项目(不建议新手使用)
vue create vue-demo
番外:
- const var let的区别
- var有设计缺陷,不建议使用
- 用const和let定义变量,const本身是常量的意思
- let 定义函数内局部变量
function xxx() {
let xxx
}
1.3声明式渲染
- Hello World示例:Vue.js 的核心是一个允许采用简洁的模板语法来声明式地将数据渲染进 DOM 的系统
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
{{ message }}
</div>
<script>
const { ref } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
const message = ref('Hello,Vue')
return {
message
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>

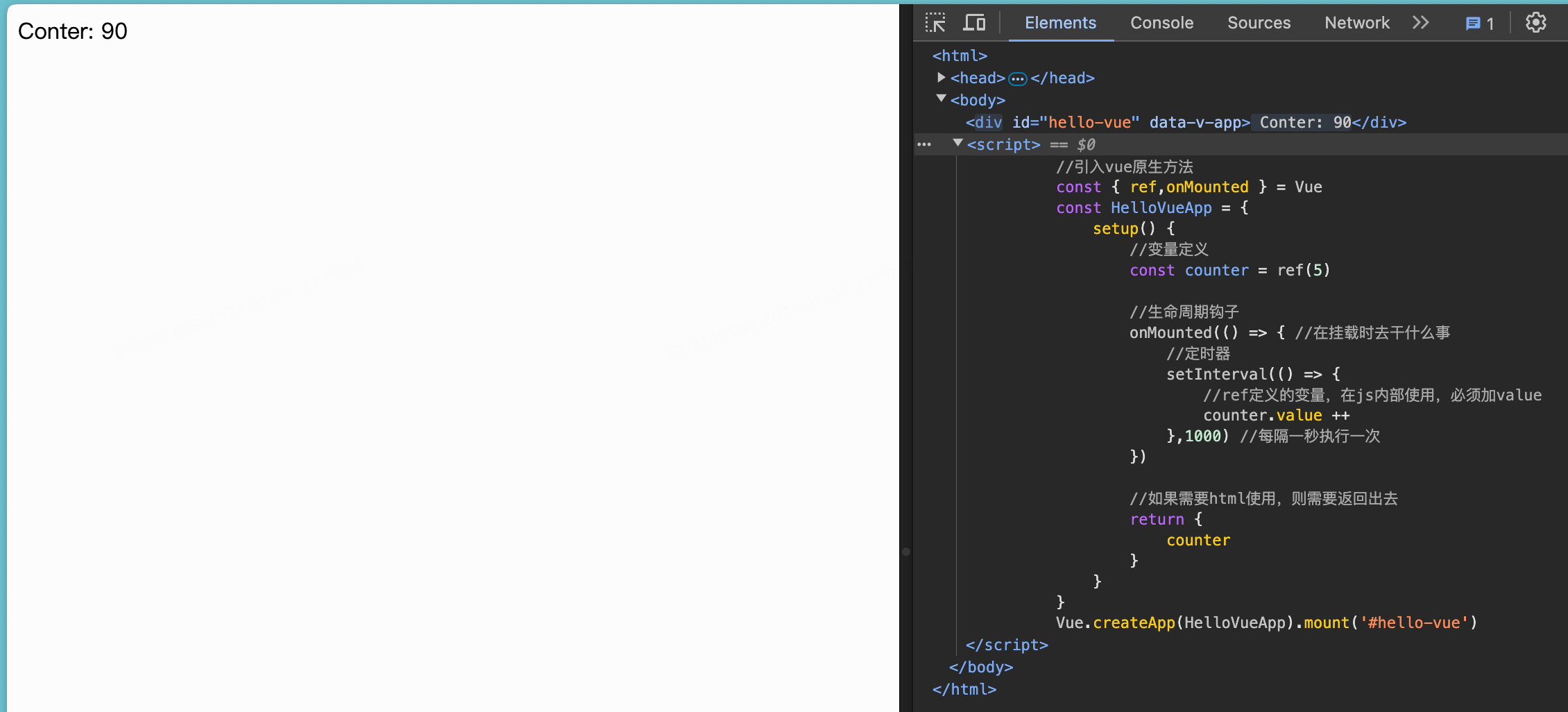
- 现在数据和DOM已经被建立了关联,所有东西都是响应式的,可通过下面示例确认:
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
Conter: {{ counter }}
</div>
<script>
//引入vue原生方法
const { ref,onMounted } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
//变量定义
const counter = ref(5)
//生命周期钩子
onMounted(() => { //在挂载时去干什么事
//定时器
setInterval(() => {
//ref定义的变量,在js内部使用,必须加value
counter.value ++
},1000) //每隔一秒执行一次
})
//如果需要html使用,则需要返回出去
return {
counter
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>
1.4模版语法
- Vue.js使用了基于HTML的模板语法,允许开发者声明式的将
DOM绑定致底层组件实例的数据,所有Vue.js的模板都是合法的HTML,所以能被遵循规范的浏览器和HTML解析器解析, - 数据绑定最常见的形式就是使用
{{ }},语法在HTML中插入文本:<span>Message:{{ msg }}</span> {{ msg }}将被替换为对应组件实例中msg属性的值,无论何时,绑定的组件实例上msg属性发生改变,传入HTML的值也会随之改变。
2.Vue3响应式
- 解决了:Vue2中新增属性,删除属性(对象),界面不会更新的问题。
- 解决了:Vue2中直接通过下标修改数组,界面不会刷新的问题。
2.1ref函数(基本数据类型的定义)
- 作用:定义一个响应式的数据即变量(基本类型)。
- 语法:
let a = ref('Hello Vue!') - 创建一个包含响应式数据的引用对象(reference对象)。
- JS中操作数据:
a.value - 模板中读取数据,不需要
.value,直接:<div>{{ a }}<div> - 接收的数据可以是基本类型,也可以是对象类型(自动转reactive)。
- 基本类型的数据:响应式依然是靠
Object.defineProperty()的get与set完成的(vue2响应式的实现方式)。 - 对象类型的数据:内部使用了Vue3中的一个新函数:reactive函数
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
{{ message }}
</div>
<script>
const { ref } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
const message = ref('Hello,Vue')
return {
message
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>
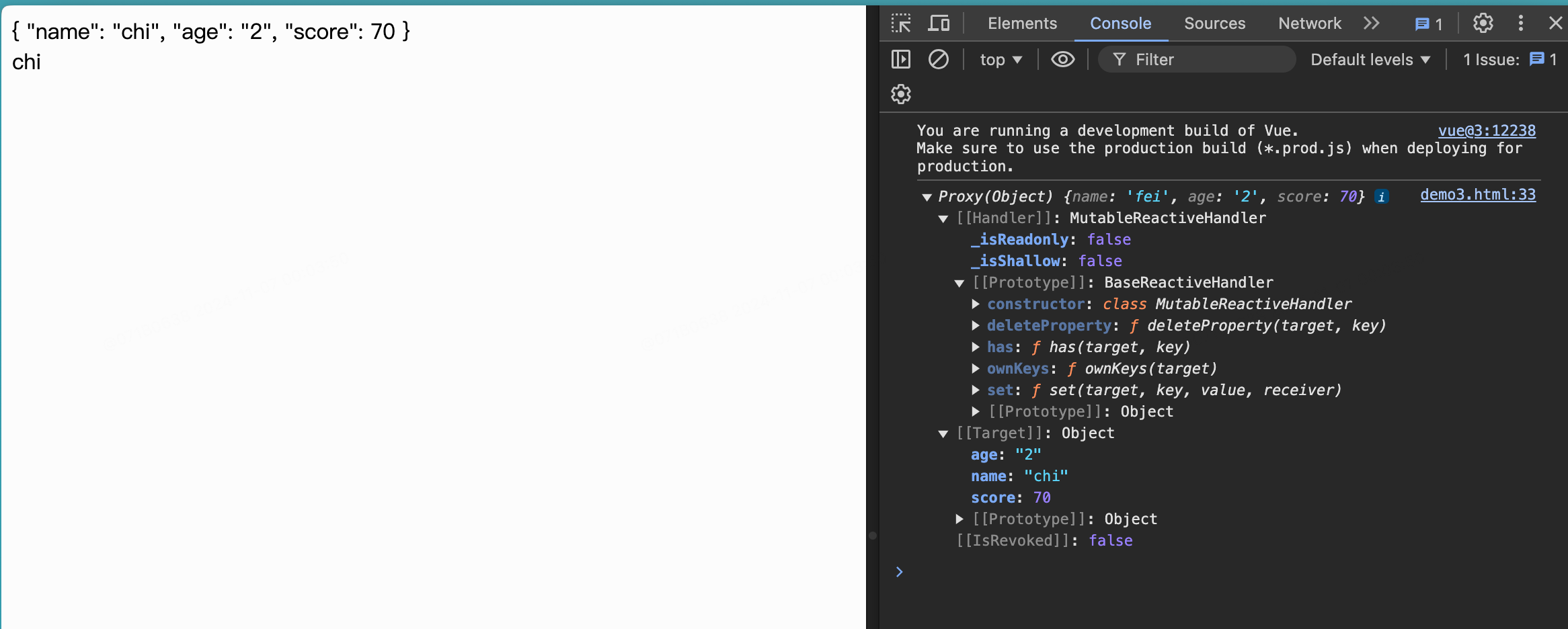
2.2reactive函数
- 作用:定义一个对象类型的响应式数据(基本类型数据不能用,要用ref函数)。
- 语法:const 代理对象=reactive(原函数),接收一个对象或数组,返回一个代理对象(proxy对象)。
- reactive定义的响应式数据是深层次的。
- 内部基于ES6的Proxy实现,通过代理对象操作源内部数据进行操作。
- 用法与ref创建的代理对象类似,不过操作时不需要再加.value了
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
{{ student }}
<br>
{{ student.name }}
</div>
<script>
const { ref,reactive,onMounted } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
onMounted(() => {
student.name = "chi"
})
//定义对象 reactive返回一个proxy对象,实现对象类型的响应式
//使用const定义对象,对象本身不能改变,但是对象的属性可以改变
// 错误:student = "xxx"
// 正确:student.name = "xxx"
const student = reactive({
name: "fei",
age: "2",
score:70
})
console.log(student)
return {
student
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>
3.Vue常用指令
- 指令:带有
v-前缀的特殊属性。 - 指令的作用:当表达式的值改变时,将其产生的连带影响,响应式地作用于 DOM。
3.1v-text
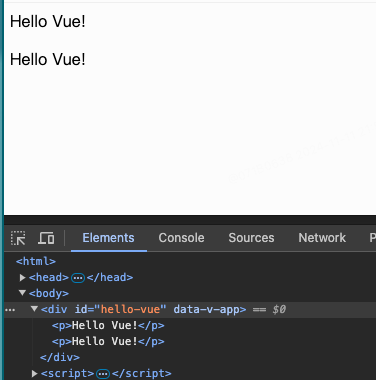
- v-text 作用与双大花括号作用一样,将数据填充到标签中。但没有闪烁问题!
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
<p v-text="msg"></p>
<!--v-text插入这个p标签的值-->
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
</div>
<script>
const { ref } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
const msg = ref("Hello Vue!")
return {
msg
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>
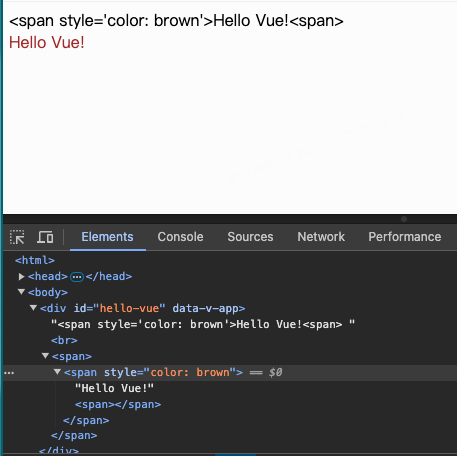
3.2v-html
- 某些情况下,从服务端请求的数据本身就是一个HTML代码,如果用双大括号会将数据解 释为普通文本,而非HTML代码,为了输出真正的HTML,需要使用
v-html指令:
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
{{ msg }}
<br>
<span v-html="msg"></span>
</div>
<script>
const { ref } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
const msg = ref("<span style='color: brown'>Hello Vue!<span>")
return {
msg
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>
3.3v-on
- 在前端开发中,我们经常监听用户发生的事件,例如点击、拖拽、键盘事件等。 在Vue中如何监听事件呢?使用
v-on指令 v-on: 冒号后面是event参数,例如click、change
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
<p>点击次数: {{ counter }}</p>
<button v-on:click="counter++">按钮</button>
<br>
<a type="text" id="fname" v-on:mouseout="counter++">鼠标离开计数</a>
</div>
<script>
const { ref } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
const counter = ref(0)
return {
counter
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>

3.4v-bind
- 用于动态绑定一个或多个属性值,或者向另一个组件传递props值(这个后面再介绍)
- 应用场景:图片地址src、超链接href、动态绑定一些类、样式等等
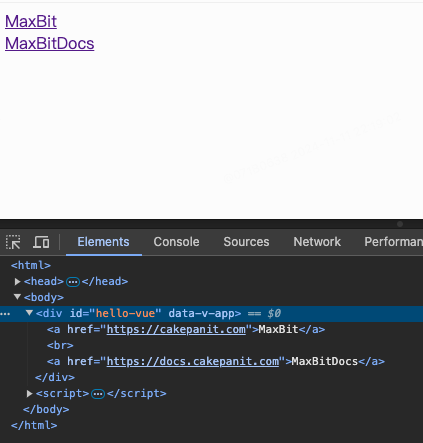
3.4.1绑定超链接
v-bind指令后接收一个参数,以冒号分割。v-bind指令将该元素的 href 属性与表达式 url 的值绑定。
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
<a href="https://cakepanit.com">MaxBit</a>
<br>
<a v-bind:href="url">MaxBitDocs</a>
</div>
<script>
const { ref } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
const url = "https://docs.cakepanit.com"
return {
url
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>
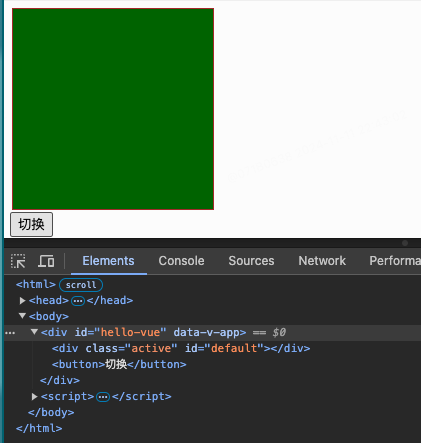
3.4.2绑定Class
- 操作元素(标签)的 class 和 style 属性是数据绑 定的一个常见需求。
- 例如希望动态切换class,为div显示不同背景颜色
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
#default {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid brown;
margin: 2px;
}
.active {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: darkgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
<!--如果isActive为true,那么class="active"属性出现-->
<div v-bind:class="{active:isActive}" id="default"></div>
<button v-on:click="Onclick()">切换</button>
</div>
<script>
const { ref } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
const isActive = ref(false)
function Onclick(){
if (isActive.value) {
isActive.value = false
} else {
isActive.value = true
}
}
return {
isActive,
Onclick
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>
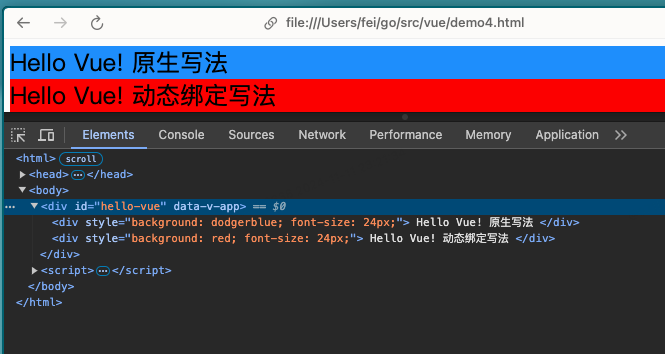
3.4.3绑定Style
v-bind:style的对象语法看着非常像 CSS,但其实是一个 JavaScript 对象。- 可以使用v-bind在style样式中传递样式变量。
- 使用时需要将css样式名中带”-“的转成驼峰命名法,如font-size,转为fontSize
- 例如后台管理系统中改变侧边栏宽度
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
<div style="background: dodgerblue;font-size: 24px">
Hello Vue! 原生写法
</div>
<div v-bind:style="{background: color,fontSize: num + 'px'}">
Hello Vue! 动态绑定写法
</div>
</div>
<script>
const { ref } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
const color = ref('red')
const num = 24
return {
color,
num
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>
3.4.4指令缩写
-
v-前缀作为一种视觉提示,用来识别模板中 Vue 特定的 属性。 但对于一些频繁用到的指令来说,就会感到使用繁琐。 -
因此,Vue 为 v-bind 和 v-o n 这两个最常用的指令,提供了特定简写: v-bind 缩写
-
v-bind缩写
<!--完整语法-->
<a v-bind:href="url"> ... </a>
<!--缩写-->
<a :href="url"> ... </a>
<!--动态参数的缩写-->
<a :[key]="url"> ... </a>
v-on缩写
<!--完整语法-->
<a v-on:click="doSomething"> ... </a>
"<!--缩写-->
<a @click="doSomething"> ... </a>
<!--动态参数的缩写-->
<a @[event]="doSomething"> ... </a>
4.Vue常用属性
4.1setup函数
- setup是vue3中的一个全新的配置项,值为一个函数。
- setup是所有CompositionAPI(组合API)的基础,组件中所用到的数据、方法等都需要在setup中进行配置。
- setup中的两种返回值:
- 若返回一个对象,则对象中的属性,方法,在模板中都可以使用。
- 若返回一个渲染函数(html):可以定义渲染内容。
import { h } from 'vue'
...
setup() {
...
return () ==> h('h1','学习')
}
- setup执行的时机:在 beforeCreate(vue实例创建) 之前执行一次,this 是 undefine。
- setup的参数
- props:值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,且组件内部声明接收了的属性。
- context:上下文对象
- attrs:值为对象,包含组件外部传递过来,但没有在props配置中声明的属性。
- slots:收到的插槽内容,想到相当于this.$slots。
- emit:分发自定义事件的函数,相当于this.$emit。
- 注意点:
- 尽量不要与Vue2配置混用。
- Vue2配置(data,methos,computed…)中可以访问到 setup 中的属性,方法。
- 但setup中不能访问到vue2配置(data,methos,computed…)。
- 如果重名,setup中的优先。
- setup不能是 async 函数,因为返回值不再是return的对象,而是 promise,模板中看不到 return 对象中的属性。
- 尽量不要与Vue2配置混用。
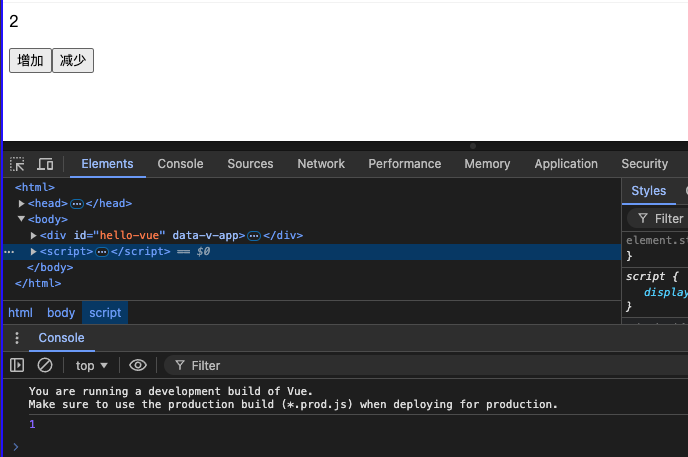
4.2方法
- 使用function关键字定义的数据处理函数。
- 定以后在return中返回,才能在模板中使用
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
<p>{{ count }}</p>
<button @click="increment()">增加</button>
<button @click="subIncrement()">减少</button>
</div>
<script>
const { ref } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
//定义变量
const count = ref(1)
//普通方法 入参
function increment(){
count.value ++
}
//箭头函数 入参
const subIncrement = (()=> {
count.value --
})
return {
count,
increment,
subIncrement
}
}
}
//用vue实例调用方法
const vm = Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
console.log(vm.count)
vm.increment()
vm.increment()
vm.subIncrement()
</script>
</body>
</html>
4.3计算属性
- 计算属性(computed):根据所依赖的数据动态显示新的计算结果。
- 示例:需要在 {{ }} 里添加计算再展示数据,例如统计分数
- 数值计算一般用法:
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
<span>总分:{{ math + chinese + english }}</span>
</p>
<span>总分:{{ sum }}</span>
</p>
<span @click="sumFunc()">总分:{{ sum1 }}</span>
</div>
<script>
const { ref,computed } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
//方式1
const math = ref(90)
const chinese = ref(101)
const english = ref(102)
//方式2,当使用了计算属性时,返回的属性名和变量名是相同的用法,在模版种用{{ }}就可以
const sum = computed(()=>{
return math.value + chinese.value + english.value
})
//方式3,函数计算
const sum1 = ref(0)
function sumFunc(){
sum1.value = math.value + chinese.value + english.value
}
return {
math,chinese,english,sum,sum1,sumFunc
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>

- computed计算属性用法:
- 小结:计算属性一般就是用来通过其他的数据算出一个新数据,而且它有一个好处就是, 它把新的数据缓存下来了,当其他的依赖数据没有发生改变,它调用的是缓存的数据,这 就极大的提高了我们程序的性能。而如果写在function里,数据根本没有缓存的概念,所 以每次都会重新计算。这也是为什么不用function的原因!
4.4监听属性
- 监听属性(watch):是一个观察动作,监听data数据(setup中的变量)变化后触发对应函数,函数有newValue (变化之后结果)和oldValue (变化之前结果)两个参数。 当需要在数据变化时执行异步或开销较大的操作时, 这个方式是最有用的。
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="hello-vue">
<p @click="change()">消息:{{ msg }}</p>
<p>观察消息:{{ watchMsg }}</p>
</div>
<script>
const { ref,watch } = Vue
const HelloVueApp = {
setup() {
const msg = ref('hello Vue!')
const watchMsg = ref()
function change(){
msg.value = 'hello Go!'
}
//msg表示被监听的数据;newVal,oldVal是指被监听数据发生变化时,新值和旧值
watch(msg,(newVal,oldVal)=>{
console.log(newVal,oldVal)
watchMsg.value = newVal
//或者 watchMsg.value = msg.value
})
return {
msg,watchMsg,change
}
}
}
Vue.createApp(HelloVueApp).mount('#hello-vue')
</script>
</body>
</html>

常见场景:表单选择时,下面的选项依赖上面的选项。就可以使用watch监听上面的选项(如实时调借口去getlist)下面的选项。
Last updated 25 Nov 2024, 23:56 +0800 .